What is CPU – CPU is a microprocessor chip or device making all the important decisions in desktop, laptop, notebook, server, computer. Which is firmly responsible for all Windows, Unix, Linux, Mac OS computer operation, for input, output, processing, and all work to be processed by users. Here CPU abbreviated as (Central Processing Unit) all types of decision making logical, statistical, general, algebraic, numerical, text, multimedia, data, and information tasks in the computer are processed and easily executed by the CPU device. Here in each CPU, the control system activities are processed through ALU (Arithmetic Logic Unit), CU (Control Unit) operations, memory registered device used for storing and retrieving information, etc. Where every single desktop computer motherboard has at least one CPU microprocessor installed in it. Where some motherboards have two or more microprocessor CPUs installed for multiprocessing (use in servers). Where each microprocessor works with the information processed by the user between the computer hardware and software.
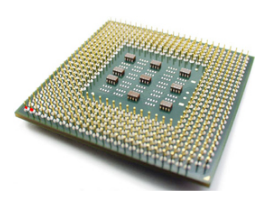
Main components of CPU.
- Alu.
- Cu.
- memory / register.
Alu – Here alu means the arithmetic logic unit (central processing unit) of the CPU or the main brain of the computer. Where the main responsibilities performed by the ALU component are arithmetic and logical data and information handling. As such, performing math operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication, division), here include logical operations, (true, false, not), statistical, algebraic, numerical, textual, multimedia, Boolean expressions, and, or, not, nand, nor, xor, XNOR gate operations, and all other remaining decisions are produced and executed by alu device. even the alu is an actual processing part or component of the microprocessor. and the alu is the system that inputs meaningful decisions or generates them.
Cu – Here cu is stands for Control Unit, where Cu controls the instructions generated by the computer microprocessors. It even controls or manages the successful operation of the computer and related activities. Where each control unit ensures that all computer hardware, software functions, work in proper sequence in the computer. It even receives instructions from the CPU, and applies them to computer operations.
Memory/Register – A register is a small memory unit installed with a computer microprocessor. which is called CPU memory or a small storage unit. It is a high-speed memory processing device register. Where all the data and information is stored and processed by each computer microprocessors in the CPU register device first from the result. Where the memory or register device distributes the processed data result to the external device and also to the media. Where the number of small registers each depends on the need of the built-in components throughout the microprocessor manufactured by the microprocessor manufacturing companies.
Pinless Processor – Pinless processor is a new generation microprocessor chip or device. It is a complete new replacement for the older Pentium One, Two, and Three, microprocessors. Where the pinless microprocessor doesn’t need to be inserted hard on the processor sockets built into the motherboard. But in pinless microprocessors, you can easily place it on a new generation computer motherboard printed circuit board easily. Where first, you remove the PCB cap, you now hold the pinless processor firmly in the PCB socket with zero insertion force, and install it into the microprocessor socket. You can even adjust the microprocessor as per the instructions given, or adjust or install it properly by looking at the notch placed on the microprocessor or PCB circuit. Now you can easily move the rotation clip, as long as the processor is installed properly. Now start the computer and wait for the microprocessor heat sink to be installed and further installation. Currently, the LGA 775 or later microprocessor socket is easily installed with ZIF (Zero Insert Force) in common pinless processors installed on all microprocessor printed circuit boards.

Type of CPU.
- Single-core microprocessor.
- Dual-core microprocessor.
- Quad-core microprocessor.
Single-Core Microprocessor – Where was the single-core microprocessor used from the year 1960 to the year 1990. Where each single-core microprocessor operated a single process and data process at a time. When a process was already in process mode in a single-core processor, it waits for another new process to finish. Here we cannot process two system operands simultaneously in a single-core processor. Where the single-core CPU produces the result with the slow process waiting for the result. Even it could not support multitasking, multiprocessing, system features. But the dual-core microprocessor in its new version was a more advanced microprocessor than a single-core CPU. where right now all current CPUs provide more dual-core processing layers of data and information at the same time.
Example of single-core cpu.

Dual-Core Microprocessor – Dual-core CPU works in two dual layers. Where each system microprocessor has two separate dual-core process paths for input and output CPU processing data and electronic information. Where it inputs and processes two or more tasks simultaneously, similar to a dual-core microprocessor CPU, as compared to single microprocessors. This means, when processing multiple tasks and jobs with the same dual-core microprocessor installed at the time, because the dual-core CPU uses two different paths for input and output programmer instructions. Where it is much faster than a single-core CPU, because a single-core single path plays the role of input or output CPU data and information. Where all modern motherboard manufacturers used to manufacture dual-core CPU sockets and microprocessors for new generation motherboards.
Example of dual-core cpu.

Quad-Core Microprocessor – A quad-core CPU is an extended version of the dual-core microprocessor. Where the dual-core microprocessor divides the processes into two parts. Where quad-core microprocessor processes data and information in dual-layer at the same time with multitasking, multiprocessing task, and multiple job process facilities. Even a quad-core microprocessor has inbuilt memory and instructions to deal with a huge amount of tasks processed simultaneously by the programmer.
Example of quad-core cpu.

Generations of Microprocessor/CPU.
- Pentium Microprocessor/CPU.
- Celeron Microprocessor / CPU.
- Xeon Microprocessor/CPU.
- Intel i3 Microprocessor/CPU.
- Intel i5 Microprocessor/CPU.
- Intel i7 Microprocessor/CPU.
Pentium Microprocessor – Pentium is a popular class of microprocessors. Where the Pentium microprocessor was introduced by the Intel company in 1993. Here the 32-bit microprocessor Pentium 4 processor is the new expanded version of the earlier Pentium 1 and Pentium 2,3 CPUs. Here the Intel company widely produced Pentium microprocessors for desktop, laptop, and notebook computers after 1993. It soon became more popular due to its tremendous performance. As multi-tasking, multi-processing, and multi-threading, it became popular with more processing capabilities, all types of computers process data and information depending on the needs of the user on the processor’s capacity.

Celeron Microprocessor – Celeron microprocessor was introduced by Intel company after the year 1998. Where it was completely inspired by the concept of the Intel Pentium microprocessor. But it was slow only at processing speeds of about 200 Mhz, 300 Mhz, and 500 Mhz, 900 Mhz MHz. Where the Celeron microprocessor was to design the Celeron microprocessors for computers designed for those people or customers. Those Pentium architecture based personal computers could not afford microprocessors. Where Celeron-based computers were available as cheaper microprocessor-based computer models than other computer Pentiums or other computer brands.

Xeon Microprocessor – The Xeon Microprocessor is a processor belonging to the Intel microprocessor family. Where client and server platforms are the main reason for designing Xeon processors for computers to have a high speed with accuracy and reliability. Where the inbuilt cache memory is more in Xeon-based microprocessors than in the previously released intel processors. Even the big advantage of the Xeon microprocessor is that, this microprocessor is extremely heavy-duty, and is the only microprocessor to last long based on input functions.

Athlon Microprocessor – Athlon Microprocessor is introduced by AMD (Advanced Micro-device) company. Which are capable of designing Intel-enabled microprocessors with similar capabilities. Where AMD company introduced a 200 MHz processor in the year 1999. Similarly for 32-bit Windows operating systems, the 650 MHz speed supports the operating system. Where the AMD Athlon microprocessor has additional cache memory to deal with multitasking processing, and multiprogramming in networking mode, it is easier to perform server operations. Where the AMD microprocessor clock speed is more influential than its generation compared to the microprocessor list. Even current AMD processors are fully capable of handling all Windows, Apple Mac, Linux, Android operating systems 32-bit and 64-bit operations.

Intel Core i3 CPU – Intel Core i3 CPU is an Intel microprocessor based on a laptop, desktop, and ultra-book. Even for mobile users, the dual-core family is the cheaper and more advanced processor device related to 64-bit and x86 based microprocessor design. Where Intel Core i3 processor was launched by Intel company in the year 2010. The major advantage of using the Intel Core i3 microprocessor here is a large amount of inbuilt cache memory with this microprocessor for multi-layer task processing deals with multitasking, multiprocessing, multithreading, or multi-processing. Even Intel Core i3 microprocessor supports better web surfing, internet web browsing, networking, client, server, multimedia, graphics, games, movies, and data processing smoothly. Here it means that, you don’t need to install or attach additional hardware with Intel Core i3 microprocessor.

Intel Core i5 CPU – The Intel Core i5 microprocessor belongs to the Intel dual-core family. This is a newer microprocessor technology better than the Core i3 microprocessor. But the processing capacity is less than the Intel Core i7 microprocessor. Where it supports Hyper-Threading technology with enhanced Intel Speed Step with Turbo Boost. Where Intel Core i5 includes integrated graphics processor features to deal with graphical processing applications. Where it meets with high cache memory multi-layer cores for handling multitasking and multi-processing tasks. Where the Intel Core i5 microprocessor optimally supports high-quality video and gaming operation for game, multimedia, graphics, networking, and server operation.

Core i7 CPU – The Intel Core i7 microprocessor belongs to the Intel quad-core processor family. Where it is the top-of-the-line series microprocessor design by Intel Corporation. Where Intel Core i7 processor is better than Intel Core i5 and Intel Core i3 microprocessor. Here the Intel Core i7 CPU has Hyperthreading, increased Intel processing speed with Turbo Boost features. Which makes the Intel Core i7 processor different from other lineup company’s microprocessors. Even Intel Core i7 microprocessor handles high graphical applications with HD multimedia support, networking support easily. Where you can manage Windows Multitasking, Multiprocessing, Client-Server Order Enabled, High Definition Visual Graphic Animated 4th Generation Protected Tasks more optimally in an Intel Core i7 microprocessor. But Intel Core i7 microprocessor is much more expensive than the Intel Core i5 and Intel Core i3 microprocessor.






























































































































































A very informationrmative story and lots of really honest and forthright comments made! This certainly got me thinking about this issue, cheers all.
The way you write, you are really a professional blogger.:~,-’