Introduction
In the previous class, we studied many different types of shapes such as triangles, squares, rectangles, quadrilaterals, etc., and formulae to find their areas. We have already studied how to find the area of a triangle if its base and height are given. We use the formula written below to find the area.
Area of a triangle = ½ × Base × Height
This formula is directly useful for right-angled triangles. How can we find the area of any other triangle if its height is not given? In this section, we shall study the formula to find the area of a triangle without using the above formula.
What is Heron’s Formula
Heron’s formula is derived by the mathematician Heron. According to Heron, if the three sides of a triangle are given then we can find its area with the help of a formula. This formula is known as Heron’s Formula.

According to the formula,
Area of a triangle = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
Where, a, b, and c = sides of the triangle
s = semi-perimeter of the triangle = (a + b + c)/2
Note – 1) Semi-perimeter of the triangle is half the perimeter of the triangle.
2) The three sides of the triangle are a, b, and c. Where side a represents the side opposite to vertex A means BC. Similarly, sides b and c represent the sides opposite to vertex B and C means AC and AB respectively.
3) Heron’s formula is useful when the height of the triangle is not given or cannot be found easily.
Area of Triangle by Heron’s Formula
With the help of Heron’s formula, we can easily find the area of a triangle. In any triangle, if all three sides are given then first, we find the semi-perimeter and then we use the formula. Let us understand with the help of an example.
Example – Find the area of the triangle whose three sides are 3 cm, 5 cm, and 6 cm.
Solution – Let three sides be a = 3 cm, b = 5 cm, and c = 6 cm.
Semi-perimeter of the triangle, s = (a + b + c)/2 = (3 + 5 + 6)/2 = 14/2 = 7 cm
Now, area of the triangle = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
= √7(7 – 3)(7 – 5)(7 – 6)
= √7(4)(2)(1)
= √7×2×2×2×1
= 2√7×2×1
= 2√14 sq. cm. Ans.
Note – We know that a triangle with all three sides of different measurements is Scalene Triangle. In the above example, the given triangle is a scalene triangle.
Area of an Isosceles Triangle by Heron’s Formula
If two sides of the given triangle are equal then that is an Isosceles Triangle. We can compress the formula to find the area of an isosceles triangle. Let’s see how can we do it.
Let △ABC be an isosceles triangle and its sides are a, b, and b. In this isosceles △ABC, sides AB and AC are equal sides.
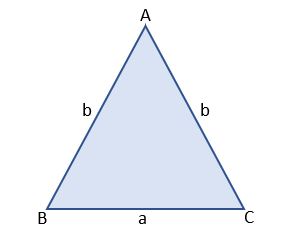
First of all, we shall find the semi-perimeter of the isosceles △ABC.
Semi-perimeter of isosceles △ABC, s = (a + b + b)/2 = (a + 2b)/2
Now, area of isosceles △ABC = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – b)
= √s(s – a)(s – b)2
= (s – b)√s(s – a)
Since s = (a + 2b)/2 therefore,
= {(a + 2b/2) – b}√{(a + 2b)/2}[{(a + 2b)/2} – a]
= {(a + 2b – 2b)/2}√{(a + 2b)/2}[{(a + 2b – 2a)/2}]
= (a/2)√{(a + 2b)/2}[{(2b – a)/2}]
= (a/2)√{(2b + a)/2}{(2b – a)/2}
= (a/2)√[{(2b)2 – a2}/4]
= (a/2)(1/2)√{4b2 – a2}
= (a/4)√(4b2 – a2)
Area of an isosceles triangle = (a/4)√(4b2 – a2)
In the above formula, b is the equal side of the isosceles triangle. This formula is very helpful to find the area of an isosceles triangle without finding the semi-perimeter. We can directly use this formula to solve the questions related to isosceles triangles.
Area of an Equilateral Triangle by Heron’s Formula
The triangle with all three sides of equal measure is an Equilateral Triangle. We can minimize the formula to find the area of an equilateral triangle. Let’s see how can we do it.
Let △ABC be an equilateral triangle and its three sides are a, a, and a.

First of all, we shall find the semi-perimeter of the equilateral △ABC.
Semi-perimeter of equilateral △ABC, s = (a + a + a)/2 = 3a/2
Now, area of equilateral △ABC = √s(s – a)(s – a)(s – a)
= √s(s – a)(s – a)2
= (s – a)√s(s – a)
Since s = 3a/2 therefore,
= (3a/2 – a)√(3a/2)(3a/2 – a)
= {(3a – 2a)/2}√(3a/2){(3a – 2a)/2}
= (a/2)√(3a/2)(a/2)
= (a/2)√(3a2/4)
= (a/2)(a/2)√3
= (a2/4)√3
Area of an equilateral triangle = (a2/4)√3
In the above formula, a is the equal side of the equilateral triangle. We can use the above formula to find the area of an equilateral triangle without finding the semi-perimeter. The formula can be directly used if the side of the equilateral triangle is given.
Examples
Example (1) If the two sides of a triangle are 7 cm and 10 cm and the perimeter is 30 cm. Then find the area of the triangle.
Solution – Let the two sides of the triangle be a = 7 cm and b = 10 cm and the third side be c.
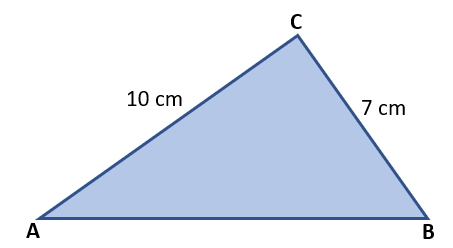
According to the question, the perimeter of the triangle = 30 cm.
Or we can also write, a + b + c = 30 cm
7 + 10 + c = 30
17 + c = 30
c = 30 – 17
c = 13 cm
Now, area of the triangle = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
Here, s (semi-perimeter) = a+b+c / 2 = 30/2 = 15 cm
Area of the triangle = √15(15 – 7)(15 – 10)(15 – 13)
= √15(8)(5)(2)
= √3×5×2×2×2×5×2
= 5×2×2√3
= 20√3 cm2
Therefore, the area of the triangle is 20√3 cm2. Ans.
Example (2) The sides of a triangular table are in the ratio of 3 : 5 : 7 and its perimeter is 300 cm. Find its area.
Solution – Let the sides of a triangular table be 3x, 5x and 7x in centimeters.
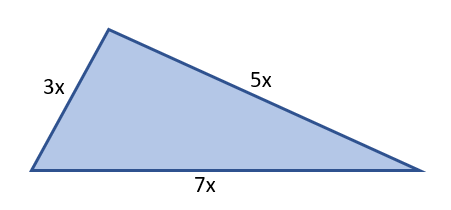
Then, the perimeter of the triangle = 3x + 5x + 7x = 300 cm (given)
15x = 300
x = 300/15
x = 20
So, the sides of the triangle are 3x = 3×20 = 60 cm
5x = 5×20 = 100 cm
7x = 7×20 = 140 cm
Semi-perimeter (s) = 60+100+140 / 2 = 300/2 = 150 cm
Now, the area of the triangle = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
= √150(150 – 60)(150 – 100)(150 – 140)
= √150(90)(50)(10)
= √150×90×50×10
= √2×3×5×5×2×3×3×5×2×5×5×2×5
= 2×2×3×5×5×5√3
= 1500√3 cm2
Therefore, the area of the triangular table is 1500√3 cm2. Ans.
Example (3) An isosceles triangle has three sides of measure 2 cm, 5 cm and 5 cm. Find its area.
Solution – Let the sides of the isosceles triangle be a = 2 cm and b = 5 cm.
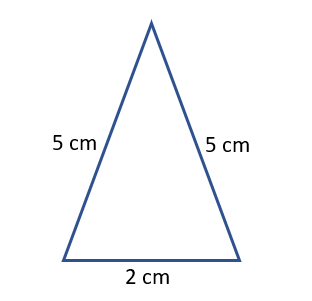
Now, the area of the isosceles triangle by Heron’s formula = (a/4)√(4b2 – a2)
= (2/4)√{4(5)2 – (2)2}
= (1/2)√{4×25 – 4}
= (1/2)√{100 – 4}
= (1/2)√96
= (1/2)√16×6
= ½ × 4√6
= 2√6 cm2
Therefore, the area of the isosceles triangle is 2√6 cm2. Ans.
Note – We can also use Heron’s main formula to find the area of an isosceles triangle.
Example (4) Each side of an equilateral triangle-shaped park is 80 meters. Find its area.
Solution – Let each side of the equilateral triangle-shaped park be a = 80 meters.

Now, Area by Heron’s formula = (a2/4)√3
= {(80)2/4}√3
= {6400/4}√3
= 1600√3 m2
Therefore, the area of the equilateral triangle-shaped park is 1600√3 m2. Ans.
Note – We can also use Heron’s main formula to find the area of an equilateral triangle.
Applications of Heron’s Formula
In the applications of Heron’s formula, we’ll find the areas of different quadrilaterals by dividing them into triangular parts. We’ll use the same heron’s formula to find the area of these triangular parts. Let’s understand with the help of some examples based on it.
Example (1) Find the area of a park PQRS, in which ∠R = 90°, PQ = 12 m, QR = 15 m, RS = 8 m and PS = 7 m.
Solution –
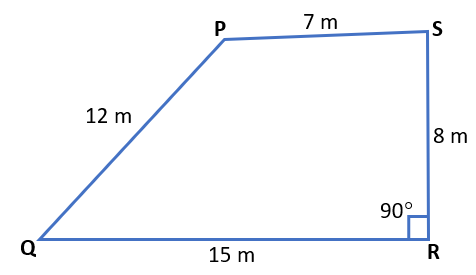
To divide this park PQRS into two triangular parts, we join point Q to point S.
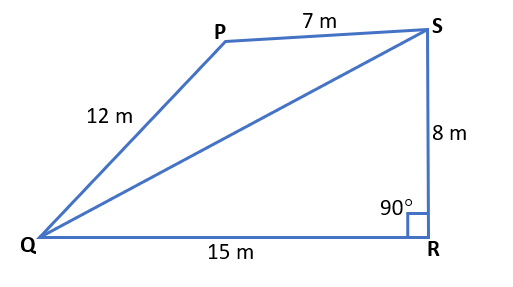
After joining QS, we can see that one of these triangular parts is the right-angled triangle. Now, we can find the measure of side QS by Pythagoras theorem.
In △QRS, by Pythagoras theorem,
QS2 = QR2 + RS2
QS2 = (15)2 + (8)2
QS2 = 225 + 64
QS = √289
QS = 17 m
Now, the area of △PQS by Heron’s formula which is a scalene triangle having sides 12 m, 17 m and 7 m.
First, semi-perimeter (s) = 12+17+7 / 2 = 36 / 2 = 18 m
area of △PQS = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
= √18(18 – 12)(18 – 17)(18 – 7)
= √18(6)(1)(11)
= √2×3×3×2×3×11
= 2×3√3×11
= 6×√3×√11
= 6×1.73×3.32
= 34.46 m2 (Approximately)
Now, the area of △QRS which is a right-angled triangle having base QR = 15 m and height RS = 8 m.
area of △QRS = ½ × base × height
= ½ × 15 × 8
= 15 × 4
= 60 m2
The total area of the park PQRS = area of △PQS + area of △QRS
= 34.46 + 60
= 94.46 m2
Therefore, the area of the park PQRS is 94.46 m2. Ans.
Example (2) In a quadrilateral ABCD, AB = 4 cm, BC = 5 cm, CD = 5 cm, DA = 6 cm and AC = 7 cm. Find its area.
Solution –
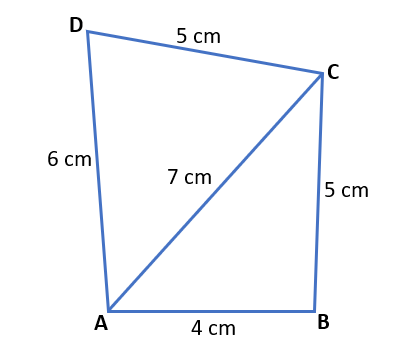
In quadrilateral ABCD, we can see there are two triangles △ABC and △ACD. Both are scalene triangles. We’ll use Heron’s formula to find the area of both.
First, the area of △ABC having sides 4 cm, 5 cm and 7 cm.
Here, semi-perimeter (s) = 4+5+7 / 2 = 16/2 = 8 cm
Now, area = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
= √8(8 – 4)(8 – 5)(8 – 7)
= √8(4)(3)(1)
= √2×2×2×2×2×3
= 2×2√2×3
= 4√6 cm2
The area of △ACD having sides 7 cm, 5 cm and 6 cm.
Semi-perimeter (s) = 7+5+6 / 2 = 18/2 = 9 cm
Now, area = √s(s – a)(s – b)(s – c)
= √9(9 – 7)(9 – 5)(9 – 6)
= √9(2)(4)(3)
= √3×3×2×2×2×3
= 3×2√2×3
= 6√6 cm2
Total area of the quadrilateral ABCD = area of △ABC + area of △ACD
= 4√6 + 6√6
= 10√6
= 10×2.449
= 24.49 cm2 (Approximately)
Therefore, the area of the quadrilateral ABCD is 24.49 cm2. Ans.