Types of network communication media and network topology.
- Twisted pair.
- Coaxial wire.
- Fiber optic cable.
Twisted pair – twisted pair cable was commonly used in the 90s to connect the internet via telephone wire to dial up internet connection network connections. Where twisted pair cable joins two insulated cooper wires together in a twisted manner. Here the advantage of twisting two wires in a twisted pair cable is that it reduces communication error and fast transmission of telephone signals. Where twisted pair was used in traditional pstn (public switched telephone service) services. Where twisted pair is generally divided into two categories. Those are called stp (shielded twisted pair) or utp (shielded pair). Now we will describe them briefly in the next section.

The advantage of twisted pair cable.
- A twisted pair cable is cheaper than other transmission cables, more easy to maintain or implement.
- Twisted pair cable has less communication interference.
- The current new twisted pair cable reduces transmission noise.
- Some twisted cable versions have faster data access rates.
- Here twisted pair transmits both analog and digital signals in the network.
- If some part of the twisted pair cable is damaged. So it does not affect the whole network system.
The disadvantage of the twisted pair.
- Twisted pair cable has slow performance weak signal carry transmission rate.
- A twisted pair cable has a higher attenuation ratio.
- Low signal data transmission bandwidth comparison with other cable media.
- It provides a low-security level.
- Here the network loss affects the part of the network easy to break.
- Designing twisted pair cable networks are complex.
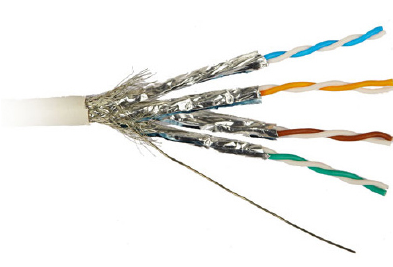
Type of twisted pair – here you see the joint picture below. Which represents the type of twisted pair cable. Where these cables are used to connect over ethernet or local area networks between a company, home, industry, or organization. Where it serves the purpose of each cable design network industries. Where shielded twisted pair or unshielded twisted pair are two common network cable categories. Which are used for many networking purposes at different places.

Shielded twisted pair – stp is abbreviated as shielded twisted pair cable. Where stp cable consists of two copper wires. It is shielded together in a helical manner. Where both copper wire insulation materials are coated with insulated materials to protect the shielded copper wire to reduce electromagnetic interference. Or it provides higher pstn data transfer rates than unshielded twisted pair cables. Where each cooper wire is shielded together with the shielded material.
Advantage of shielded twisted pair cable.
- Shielded twisted pair has more bandwidth.
- The noise is less rational.
- Reduces cross talk.
- Minimizes communication interference.
Unshielded twisted pair – utp is abbreviated as unshielded twisted pair cable. Where utp cable consists of two unshielded copper wires that are twisted together from beginning to end. Where the unshielded twisted pair cable cover is open with a plastic wire cap or cover. Where each wire is used to connect local area network components to share resources between connected network devices. Even without shielded cable bandwidth normal transmission is slow. But cheap in price or old transmission technology transfers slow data.

Advantages of unshielded twisted pair cable.
- Unshielded twisted pair has higher bandwidth.
- Unshielded twisted pair is more protective.
- Unshielded twisted pair reduces error.
- An unshielded twisted pair device improves transmission speed.
Coaxial cable – coaxial cable is another solid network cable. Which is used to transmit video-audio communication. Where the bandwidth of the coaxial cable is higher than that of the conventional twisted pair cable used. Even a commercially developed coaxial cable connects your satellite receiver antenna directly to your television set. Where your tata sky, dish tv, or maybe a company setup box wire comes from the roof of your house. Which is said to be the best example of coaxial cable. Whereas coaxial cable is another use in the network industry to connect a cable modem with broadband network service. Where the coaxial cable is surrounded by a plastic sheath. The inner side of the cover is covered with wire mesh. Which is similar to the inner side cover with a round white plastic circle. And finally, the copper wires are housed within an encased white plastic cover.

Advantages of coaxial cable.
- Coaxial cable is a common and main medium of multimedia transmission.
- Coaxial cable covers a greater distance with higher data bandwidth transmission.
- The new modification in coaxial cable is easier to implement.
- There is less noise interference in the coaxial cable.
- Coaxial cable broadband connections have a low error rate.
- The coaxial cable supports multiple channels with higher frequency.
The disadvantage of coaxial cable.
- Coaxial cable is more expensive.
- The installation process of the coaxial cable is done separately from the twisted pair.
- In coaxial cable, it is easy to damage the entire network.
Fiber optic cable – fiber optic cable is a high-speed network data transmission technology. Where it is a group of one or more threads collecting small threads of fiber to reliably send and receive electronic data. Where older cables, fiber replacements for twisted and coaxial cable wires, use optical fiber cables to send large amounts of high-speed data packets over dedicated networks at higher speeds at higher light frequencies. Even all modern networks adopt fiber optic cabling technology for data transmission for data accuracy, reliability, and flexibility in connected networks.

Some of the advantages of fiber optic.
- Improves the performance of fiber optic cabling systems.
- Fiber optic cable increases your system bandwidth.
- The fiber optic cable is immune to electronic noise.
- The amount of fiber optic cable signal attenuation will be very low.
- Fiber optic cable covers long distances at a low cost.
- Fiber optic cables have faster transmission data bandwidth.
Some disadvantages of fiber optic.
- Costly to manage, control and update fiber-optic connections, only a few people have these skills to do.
- Glass plastic wires with small thin filaments are the main cause of network down due to the high probability of breakage.
- Hard to find the best-advanced technology error, troubleshooting, problem-solving process.
- Expensive hardware equipment, not everyone can afford it for fiber cable network setup by small organizations and firms.
Types of networks.
Peer to peer network – peer to peer network is a type of internet network connection with a common network line. Where it facilitates network communication to share resources and network service between clients connected without a server. In a peer-to-peer network, all clients use central computers to process data and information. Here also each p2p client has the ability to admin computer.
Client-server network – server services are like a responder in a client-server network. Where the network subscriber is a service requester. Where client and server can be interconnected through lan (local area network) or wan (wide area network). Where commercially the reason for designing a client-server network is to share business, commercial, non-commercial, data and resources from the server to the client. Where a server is a powerful computer or machine, which already has a list of all the necessary heavy-duty hardware-software components. As such, a dbms program is a suitable program for storing information on a server machine by a client. Where the server is installed as a network administrator. Which is responsible for managing the service of all connected clients and servers. Even the client pc is operated by the network user as a workstation terminal control.

Dns – dns is abbreviated as domain name system online internet service. Here dns converts dns into internet ip address. Because dns is easy to read in the computer network, or easy technology to find linked ip address in any online internet. Where the domain name system provides the alphabetical name of any website domain. But the internet cannot process it in the same way that network switches, routers, and other network devices convert it to internet protocol format. When any website address or url is entered in the web browser address bar. So this technique immediately converts the url to the network ip address format.
Network topologies.
Bus topology – bus topology is a popular networking topology in large organizations, companies, and industries. Where in the bus topology all the computers are continuously connected to each other in the same row sequence. They are called the bus or network backbones. Where in the bus topology all the connected computers one after the other all the connected computers share the same lines to share data and valuable information.
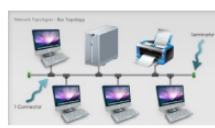
- The bus topology is very easy to implement.
- Minimum network cable required in bus topology.
- This topology has a minimum cost to set up bus topology.
- Bus topology can be used in both small and large networks.
The disadvantage of bus topology.
- Connect limited clients for better network speed in the bus topology. If you have connected more clients and nodes in this topology. So your network will be slow and down.
- When the main cable in the bus topology is damaged or the network is damaged. So the chances of a sudden shutdown of all connected client networks increase.
- Upgrading, maintenance, and troubleshooting become more important in bus topology network communications.
- Low-security network in a bus topology, leakage of information, it is difficult to control and manage service in a large bus network.
- The more computers connected to the bus network, the greater the change in network data traffic collisions and network breakdowns.
Star topology – star topology can be easily implemented in small offices, buildings, and company, areas. Here in a star topology, where all connected client cables connect to a central hub, switch, server, or main computer. Where most of the world’s computer network designers implement a normal network with star topology. This is why, each network workstation shares a different cable-medium network sharing. Generally, star topology is recommended by any new network administrator for building a network.

The benefit of star topology.
- Star topology is easier to implement than the bus, ring, graph, or mesh topologies.
- Star topology has better device network performance.
- Fast transmission is a reliable network in a star topology.
- Improves accuracy, reliability, and better communication between workstations.
- If a client fails, the network continues to operate.
- With one central computer in the star topology, all the clients can control their behavior.
- Adding new network clients, easy to maintaining clients can also easily remove a new or existing client node.
Some losses of the star topology.
- In star topology, the central computer is heavily loaded with network transmission.
- If the central computer fails in the star topology. So here all the networks will be down automatically.
- If the client computer fails to over-connect to the network. So the transmission data rate gets lower.
- Leakage of data and information security can happen in a star topology.
Ring topology – in a ring topology, where each computer is connected to two or more network nodes in the previous and next order. Which is called each connected client previous and next node. Where its shape or ring topology looks like a circle or a perfect ring. Where in ring topology two nodes on either side can transfer or share data in-ring network. where ring topology is specifically applied. When network computers need to be set up in circle or ring order. Here all the computers located in the form of the circular structure are directly or indirectly connected with pre and next-network node links. It even provides you with fast, secure, reliable, data and information network communication.
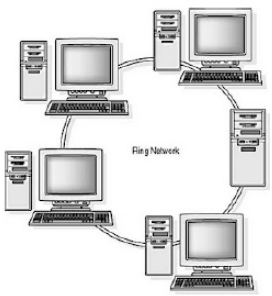
The benefit of the ring topology.
- Data and information transfer rapidly across the ring network. A central network system controls all network components in the environment.
- Network data packets are being transferred from the ring network server to the previous or next computer to all ring network client computers.
- If many more new clients are added. So ring network limit, and this network will cause slow data transmission and lack of information security issues.
- There is no network data traffic, network data conflicts, and information transmission information in the world wide web system.
Some of the losses of ring topology.
- Ring topology is difficult to manage each node and link of the ring network, troubleshooting errors, and other issues that arise during the operation of the network.
- When a new node is added to the ring network. So here the network is disturbed, or the network breaks down, it affects the rest of the network services at times when there is a conflict in the network.
- Ring networks that hold network data traffic information when sharing their resources have a single cable to use from start to endpoint.
- When the central ring network server goes down. So it will automatically close communication between all connected network devices and services.
Ethernet – local area network uses the term ethernet in-network to refer to connections and connectivity. Where an ethernet-connected node developed by xerox corporation shares high-speed network data and information at 10 mbps to 1000 mbps speed between connected network clients while sharing and receiving information with clients.

Fddi – abbreviated as fiber fddi distributes the data interface for sending digital over fiber optic cables. Where fddi is token passing networking, and it supports data rates up to 100 Mbps per second. It is used for an auxiliary backbone wide area network. Where fddi enables local area network connectivity with 100 or 200 Mbps.
Atm – atm is abbreviated as asynchronous transfer mode, high-speed networking technology. Which allows you to share data and voice over 53 bytes. Where it works in long-distance data networks. In which the OSI second layer called the data link layer (atm) controls, and manages the high-speed data and voice networks.
Intranet – the intranet is the prototype of the internet. Where the internet is a global network. Where everyone participates worldwide from different corners or places of the world. But intranet is a limited network in a single organization. Where members of the certified organization company use specialized intranet website resources similar to a local area network. Where the local intranet operates in a small geographic area with limited access for general-purpose sharing. Where the internet common use shares the common goal of a member of the company. But it is based on the common TCP/IP internet network method.





























































































































































Simply wish to say your article is as surprising. The clearness in your post is just great and i can assume you’re an expert on this subject. Fine with your permission allow me to grab your RSS feed to keep up to date with forthcoming post. Thanks a million and please keep up the rewarding work.
This is my first time go to see at here and i am truly pleassant to read everthing at one place.